Scoring
Search result scoring occurs at a query time. The result of the search request is ordered by score (relevance), with the descending sort order unless explicitly set not to do so.
Couchbase uses a slightly modified version of the standard tf-idf algorithm. This deviation is to normalize the score and is based on tf-idf algorithm.
For more details on tf-idf, refer tf-idf
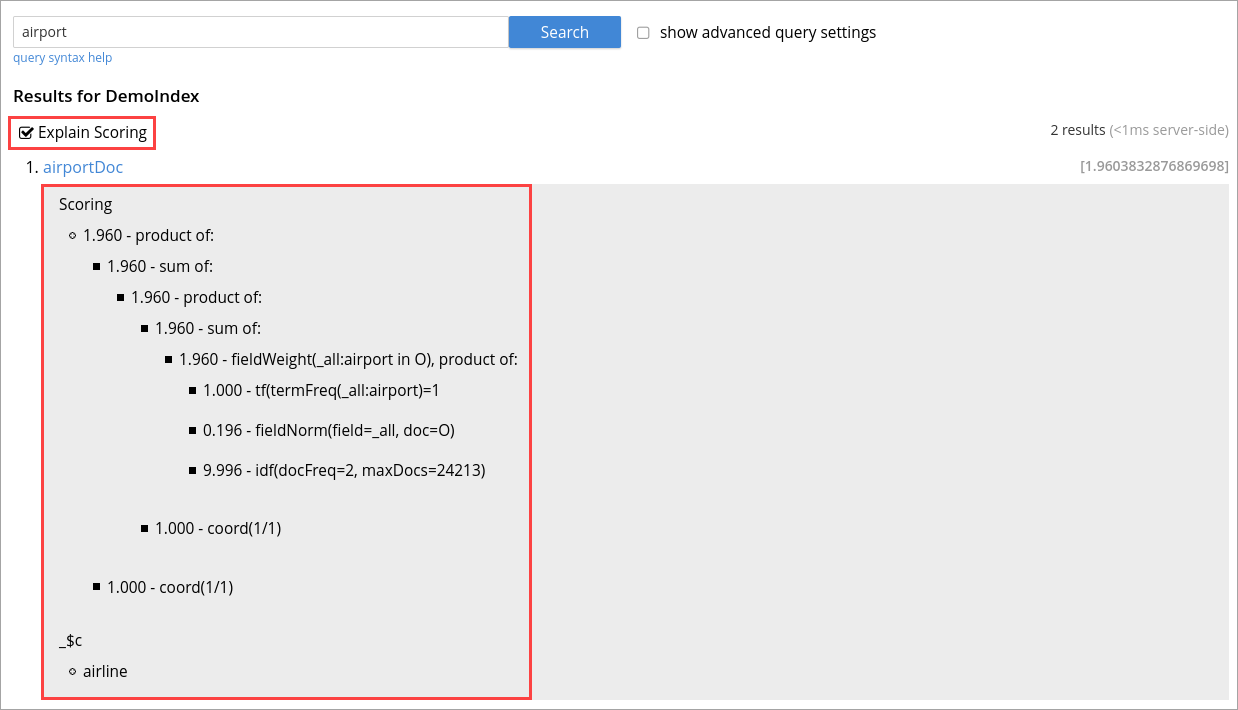
By selecting the explain score option within the search request, you can obtain the explanation of how the score was calculated for a result alongside it.
Search query scores all the qualified documents for relevance and applies relevant filters.
In a search request, you can set score to none to disable scoring by. See Score:none
Example
The following sample query response shows the score field for each document retrieved for the query request:
"hits": [
{
"index": "DemoIndex_76059e8b3887351c_4c1c5584",
"id": "hotel_10064",
"score": 10.033205341869529,
"sort": [
"_score"
],
"fields": {
"_$c": "hotel"
}
},
{
"index": "DemoIndex_76059e8b3887351c_4c1c5584",
"id": "hotel_10063",
"score": 10.033205341869529,
"sort": [
"_score"
],
"fields": {
"_$c": "hotel"
}
}
],
"total_hits": 2,
"max_score": 10.033205341869529,
"took": 284614211,
"facets": null
}tf-idf
tf-idf, a short form of term frequency-inverse document frequency, is a numerical statistical value that is used to reflect how important a word is to a document in collection or scope.
tf-idf is used as a weighting factor in a search for information retrieval and text mining. The tf–idf value increases proportionally to the number of times a word appears in the document, and it is offset by the number of documents in the collection or scope that contains the word.
Search engines often use the variations of tf-idf weighting scheme as a tool in scoring and ranking a document’s relevance for a given query. The tf-idf scoring for a document relevancy is done on the basis of per-partition index, which means that documents across different partitions may have different scores.
When bleve scores a document, it sums a set of sub scores to reach the final score. The scores across different searches are not directly comparable as the scores are directly dependent on the search criteria. So, changing the search criteria, like terms, boost factor etc. can vary the score.
The more conjuncts/disjuncts/sub clauses in a query can influence the scoring. Also, the score of a particular search result is not absolute, which means you can only use the score as a comparison to the highest score from the same search result.
FTS does not provide any predefined range for valid scores.
In Couchbase application, you get an option to explore the score computations during any search in FTS.
On the Search page, you can search for a term in any index. The search result displays the search records along with the option Explain Scoring to view the score deriving details for search hits and which are determined by using the tf-idf algorithm.

Score:none
You can disable the scoring by setting score to none in the search request. This is recommended in a situation where scoring (document relevancy) is not needed by the application.
Using "score": "none" is expected to boost query performance in certain situations.
|
Scoring Tips and Recommendations
For a select term, FTS calculates the relevancy score. So, the documents having a higher relevancy score automatically appear at the top in the result.
It is often observed that users are using Full-Text Search for the exact match queries with a bit of fuzziness or other search-specific capabilities like geo.
Text relevancy score does not matter when the user is looking for exact or more targeted searches with many predicates or when the dataset size is small.
In such a case, FTS unnecessarily uses more resources in calculating the relevancy score. Users can, however, optimize the query performance by skipping the scoring. Users may skip the scoring by passing a “score”: “none” option in the search request.