INSERT
- reference
Use the INSERT statement to insert one or more new documents into an existing keyspace. Each INSERT statement requires a unique document key and well-formed JSON as values. In Couchbase, documents in a single keyspace must have a unique key.
The INSERT statement can compute and return any expression based on the actual inserted documents.
| Use the UPSERT statement if you want to overwrite a document with the same key, in case it already exists. |
Please note that the examples below will alter the data in your sample buckets.
To restore your sample data, remove and reinstall the travel-sample bucket.
Refer to Sample Buckets for details.
|
Prerequisites
The INSERT statement must include the following:
-
Name of the keyspace to insert the document.
-
Unique document key.
-
A well-formed JSON document specified as key-value pairs, or the projection of a SELECT statement which generates a well-formed single JSON to insert. See and for details.
-
Optionally, you can specify the values or an expression to be returned after the INSERT statement completes successfully.
Security Requirements
You should have read-write permission to the keyspace, to be able to insert documents into a keyspace. Any user who has the keyspace credentials or any Couchbase administrator should be able to insert documents into a keyspace. This includes the keyspace administrator for the specified keyspace, the cluster administrator, and the full administrator roles. See Roles for details about access privileges for various administrators.
| You cannot insert documents into a SASL bucket if you have a read-only role for the SASL bucket. |
RBAC Privileges
To execute the INSERT statement, you must have the Query Insert privilege on the target keyspace.
If the statement has any SELECT or RETURNING data-read clauses, then the Query Select privilege is also required on the keyspaces referred in the respective clauses. For more details about roles and privileges, see Authorization.
RBAC Examples
For this example, set the query context to the inventory scope in the travel sample dataset.
For more information, see Query Context.
To execute the following statement, you must have the Query Insert privilege on hotel.
INSERT INTO hotel (KEY, VALUE)
VALUES ("key1", { "type" : "hotel", "name" : "new hotel" });To execute the following statement, you must have the Query Insert and Query Select privileges on hotel.
INSERT INTO hotel (KEY, VALUE)
VALUES ("key1", { "type" : "hotel", "name" : "new hotel" }) RETURNING *;To execute the following statement, you must have the Query Insert privilege on hotel and Query Select privilege on `beer-sample`.
INSERT INTO landmark (KEY foo, VALUE bar)
SELECT META(doc).id AS foo, doc AS bar
FROM `beer-sample` AS doc WHERE type = "brewery";To execute the following statement, you must have the Query Insert and Query Select privileges on hotel.
INSERT INTO hotel (KEY foo, VALUE bar)
SELECT "copy_" || meta(doc).id AS foo, doc AS bar
FROM hotel AS doc;Syntax
insert ::= 'INSERT' 'INTO' target-keyspace ( insert-values | insert-select )
returning-clause?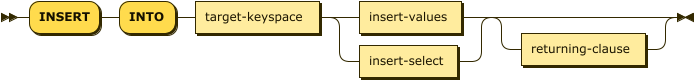
| target-keyspace | |
| insert-values | |
| insert-select | |
| returning-clause |
Insert Target
target-keyspace ::= keyspace-ref ( 'AS'? alias )?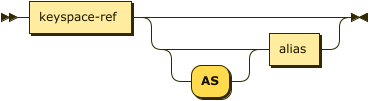
The insert target is the keyspace into which the documents are inserted. Ensure that the keyspace exists before trying to insert a document.
| keyspace-ref | |
| alias |
Keyspace Reference
keyspace-ref ::= keyspace-path | keyspace-partial
keyspace-path ::= ( namespace ':' )? bucket ( '.' scope '.' collection )?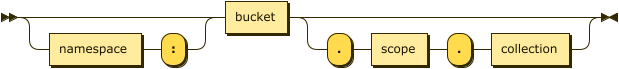
keyspace-partial ::= collection
Keyspace reference for the insert target. For more details, refer to Keyspace Reference.
AS Alias
Assigns another name to the keyspace reference. For details, refer to AS Clause.
Assigning an alias to the keyspace reference is optional.
If you assign an alias to the keyspace reference, the AS keyword may be omitted.
Insert Values
insert-values ::= ( '(' 'PRIMARY'? 'KEY' ',' 'VALUE' ( ',' 'OPTIONS' )? ')' )? values-clause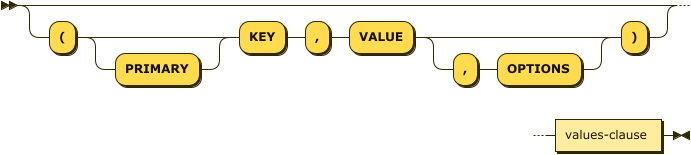
Specifies one or more documents to be inserted using the VALUES clause. Each document requires a unique key and the values must be specified as well-formed JSON.
The bracketed KEY and VALUE keywords are purely a visual mnemonic to indicate that you are setting the key and value for the inserted document. There is no syntactic requirement to include these keywords when using the Insert Values syntax. Also note that there is no syntactic difference between PRIMARY KEY and KEY.
Similarly, the OPTIONS keyword is purely a visual mnemonic to indicate that you are setting metadata for the inserted document. There is no syntactic requirement to include the OPTIONS keyword when setting metadata for the inserted document.
VALUES Clause
values-clause ::= 'VALUES' '(' key ',' value ( ',' options )? ')'
( ',' 'VALUES'? '(' key ',' value ( ',' options )? ')' )*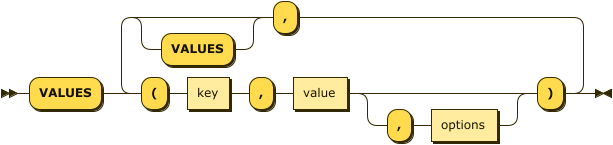
| key |
A string, or an expression resolving to a string, representing the ID of the document to be inserted. The KEY cannot be MISSING or NULL, and must be unique within the Couchbase keyspace. It can be a string or an expression that produces a string. |
| value |
A JSON object or value, or an expression resolving to a JSON object or value, representing the body of the document to be inserted. (See http://json.org/example.html for examples of well-formed JSON.) You can insert NULL, empty, or MISSING values. |
| options |
[Optional] An object representing the metadata to be set for the inserted document.
Only the
|
For examples illustrating the VALUES clause, see Examples.
Insert Select
insert-select ::= '(' 'PRIMARY'? 'KEY' key ( ',' 'VALUE' value )?
( ',' 'OPTIONS' options )? ')' select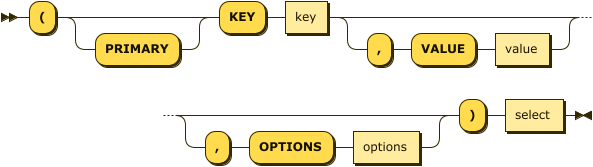
Use the projection of a SELECT statement which generates well-formed JSON to insert.
| key |
A string, or an expression resolving to a string, representing the ID of the document to be inserted. If the project of a SELECT statement generates multiple JSON documents, then your INSERT statement must handle the generation of unique keys for each of the documents. |
| value |
[Optional] An object, or an expression resolving to an object, representing the body of the document to be inserted. This may be an alias assigned by the SELECT statement. If the VALUE is omitted, the entire JSON document generated by the SELECT statement is inserted. |
| options |
[Optional] An object representing the metadata to be set for the inserted document.
Only the
|
| select |
SELECT Statement
SELECT statements let you retrieve data from specified keyspaces. For details, see SELECT Syntax.
For examples illustrating the SELECT statement, see Examples.
RETURNING Clause
returning-clause ::= 'RETURNING' (result-expr (',' result-expr)* |
('RAW' | 'ELEMENT' | 'VALUE') expr)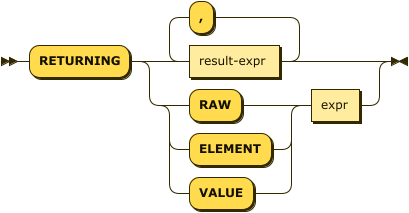
Specifies the fields that must be returned as part of the results object.
| result-expr |
Result Expression
result-expr ::= ( path '.' )? '*' | expr ( 'AS'? alias )?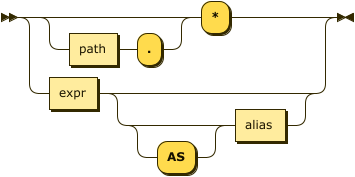
Specifies an expression on the inserted documents, that will be returned as output.
Use * to return all the fields in all the documents that were inserted.
For examples illustrating the RETURNING clause, see Examples.
Result
The INSERT statement returns the requestID, the signature, results including the keyspace and JSON document inserted, status of the query, and metrics.
-
requestID: Request ID of the statement generated by the server. -
signature: Signature of the fields specified in the returning clause. -
results: If the query specified the returning clause, then results contains one or more fields as specified in the returning clause. If not, returns an empty results array. -
errors: Returns the error codes and messages if the statement fails with errors. Returned only when the statement fails with errors. Errors can also include timeouts. -
status: Status of the statement - "successful" or "errors". -
metrics: Provides metrics for the statement such aselapsedTime,executionTime,resultCount,resultSize, andmutationCount. For more information, see Metrics.
Metrics
The INSERT statement returns the following metrics along with the results and status:
-
elapsedTime: Total elapsed time for the statement. -
executionTime: Time taken by Couchbase Server to execute the statement. This value is independent of network latency, platform code execution time, and so on. -
resultCount: Total number of results returned by the statement. In case ofINSERTwithout aRETURNINGclause, the value is0. -
resultSize: Total number of results that satisfy the query. -
mutationCount: Specifies the number of documents that were inserted by theINSERTstatement.
Monitoring
You can use the query monitoring API to gather diagnostic information.
For example, if you are performing a bulk insert using a SELECT statement, you can use the query monitoring API to get the number of documents being inserted.
Check system:active_requests catalog for more information on monitoring active queries.
For more information, see Query Monitoring.
You can also take a look at the keyspace metrics from the Web Console. To do so, go to the Data Buckets tab and click the bucket that you want to monitor. In the General Bucket Analytics screen, scroll to the Query section to gather information such as requests/sec, selects/sec and so on.
Restrictions
When inserting documents into a specified keyspace, keep in mind the following restrictions which would help avoid errors during execution.
-
The keyspace must exist. The INSERT statement returns an error if the keyspace does not exist.
-
Do not insert a document with a duplicate key. If you are inserting multiple documents, the statement aborts at the first error encountered.
-
Timeouts can affect the completion of an INSERT statement, especially when performing bulk inserts. Ensure that the timeout is set to a reasonable value that allows the bulk insert operation to complete.
To set the indexer timeout, use the REST API to set the
indexer.settings.scan_timeoutproperty. For example,curl http://localhost:9102/settings -u Administrator:password \ -d '{"indexer.settings.scan_timeout": 1200}'Use the following command to retrieve the indexer settings:
curl -X GET http://localhost:9102/settings -u Administrator:password -
When inserting multiple documents, no cleanup or rollback is done for the already inserted documents if the INSERT operations hits an error. This means, when you are inserting 10 documents, if the INSERT operation fails when inserting the 6th document, the operator quits and exits. It does not rollback the first five documents that were inserted. Nor does it ignore the failure and continue to insert the remaining documents.
Performance and Best Practices
When a single INSERT statement is executed, SQL++ prepares the statement, scans the values and then inserts the document. When inserting a large number of documents, you can improve the performance of the INSERT statement by using one of the following techniques:
-
Batching the documents to perform bulk inserts, which decreases the latency and increases the throughput. The INSERT statement sends documents to the data node in batches, with a default batch size of 16. You can configure this value using the pipeline_batch request-level parameter, or the pipeline-batch service-level setting. Note that the maximum batch size is (232 -1) and specifying a value higher than the maximum batch size may increase the memory consumption. The following example command sets the pipeline-batch size to 32 instead of the default 16:
curl -v -X POST http://localhost:8093/admin/settings -u Administrator:password \ -d '{ "debug":true, "pipeline-batch": 32 }' -
Use the max_parallelism request-level parameter, or the max-parallelism service-level setting when inserting multiple documents.
-
When performing bulk inserts, use prepared statements or multiple values.
-
When new documents are inserted, the indexes are updated. When a large number of documents are inserted, this may affect the performance of the cluster.
Examples
To try the examples in this section, set the query context to the inventory scope in the travel sample dataset.
For more information, see Query Context.
The following statement inserts a single JSON document into the airline keyspace with key "k001".
The returning clause specifies the function META().id to return the key of the inserted document (metadata), and the wildcard (*) to return the inserted document.
INSERT INTO airline ( KEY, VALUE )
VALUES
(
"k001",
{ "id": "01", "type": "airline"}
)
RETURNING META().id as docid, *;{
"requestID": "df5846b1-1044-4b1f-ae8a-979be25282d1",
"signature": {
"*": "*",
"docid": "json"
},
"results": [
{
"airline": {
"id": "01",
"type": "airline"
},
"docid": "k001"
}
],
"status": "success",
"metrics": {
"elapsedTime": "6.916ms",
"executionTime": "6.6224ms",
"resultCount": 1,
"resultSize": 117,
"serviceLoad": 4,
"mutationCount": 1
}
}The simplest use case of an INSERT statement is to insert a single document into the keyspace.
Insert a new document with key "1025" into the airline keyspace.
INSERT INTO airline (KEY,VALUE)
VALUES ( "1025",
{ "callsign": "MY-AIR",
"country": "United States",
"iata": "Z1",
"icao": "AQZ",
"id": "1011",
"name": "80-My Air",
"type": "airline"
} )
RETURNING *;{
"requestID": "c3bd0276-5d7d-425f-98f9-b333b9ae4302",
"signature": {
"*": "*"
},
"results": [
{
"airline": {
"callsign": "MY-AIR",
"country": "United States",
"iata": "Z1",
"icao": "AQZ",
"id": "1011",
"name": "80-My Air",
"type": "airline"
}
}
],
"status": "success",
"metrics": {
"elapsedTime": "5.9133ms",
"executionTime": "5.6264ms",
"resultCount": 1,
"resultSize": 254,
"serviceLoad": 4,
"mutationCount": 1
}
}You can batch insert multiple documents using multiple VALUES clauses. The VALUES keyword itself is optional in the second and later iterations of the clause.
Insert two documents with key "airline_4444" and "airline_4445" into the airline keyspace:
INSERT INTO airline (KEY,VALUE)
VALUES ( "airline_4444",
{ "callsign": "MY-AIR",
"country": "United States",
"iata": "Z1",
"icao": "AQZ",
"name": "80-My Air",
"id": "4444",
"type": "airline"} ),
VALUES ( "airline_4445",
{ "callsign": "AIR-X",
"country": "United States",
"iata": "X1",
"icao": "ARX",
"name": "10-AirX",
"id": "4445",
"type": "airline"} )
RETURNING *;{
"requestID": "2fabc03a-ea9b-49fd-a044-6ef667381311",
"signature": {
"*": "*"
},
"results": [
{
"airline": {
"callsign": "MY-AIR",
"country": "United States",
"iata": "Z1",
"icao": "AQZ",
"id": "4444",
"name": "80-My Air",
"type": "airline"
}
},
{
"airline": {
"callsign": "AIR-X",
"country": "United States",
"iata": "X1",
"icao": "ARX",
"id": "4445",
"name": "10-AirX",
"type": "airline"
}
}
],
"status": "success",
"metrics": {
"elapsedTime": "5.7617ms",
"executionTime": "5.4635ms",
"resultCount": 2,
"resultSize": 505,
"serviceLoad": 4,
"mutationCount": 2
}
}You can specify a key using an expression, as shown here.
INSERT INTO airline ( KEY, VALUE )
VALUES ( "airline" || TOSTRING(1234),
{ "callsign": "" } )
RETURNING META().id;If you don’t require the document key to be in a specific format, you can use the function UUID() to generate a unique key, as shown here.
INSERT INTO airline ( KEY, VALUE )
VALUES ( UUID(),
{ "callsign": "" } )
RETURNING META().id;Since the document key is auto-generated, you can find the value of the key by specifying META().id in the returning clause.
INSERT INTO airline (KEY, VALUE)
VALUES ( "airline::432",
{ "callsign": "",
"country" : "USA",
"type" : "airline"} )
RETURNING *;[
{
"airline": {
"callsign": "",
"country": "USA",
"type": "airline"
}
}
]INSERT INTO airline (KEY, VALUE)
VALUES ( "airline::1432",
{ "callsign": NULL,
"country" : "USA",
"type" : "airline"} )
RETURNING *;[
{
"airline": {
"callsign": null,
"country": "USA",
"type": "airline"
}
}
]INSERT INTO airline (KEY, VALUE)
VALUES ( "airline::142",
{ "callsign": MISSING,
"country" : "USA",
"type" : "airline"} )
RETURNING *;[
{
"airline": {
"country": "USA",
"type": "airline"
}
}
]INSERT INTO hotel (KEY, VALUE)
VALUES ( "1021",
{ } )
RETURNING *;Insert a document into the airline keyspace using an expiration of 5 days.
INSERT INTO airline (KEY, VALUE, OPTIONS)
VALUES ( "airline::ttl",
{ "callsign": "Temporary",
"country" : "USA",
"type" : "airline" },
{ "expiration": 5*24*60*60 } );INSERT INTO airline (KEY, VALUE)
VALUES ( "airline_24444",
{ "callsign": "USA-AIR",
"country" : "USA",
"type" : "airline"})
RETURNING META().id as docid, country;[
{
"country": "USA",
"docid": "airline_24444"
}
]Use the UUID() function to generate the key and show the usage of the RETURNING clause to retrieve the generated document key and the last element of the callsign array with an expression.
INSERT INTO airline (KEY, VALUE)
VALUES ( UUID(),
{ "callsign": [ "USA-AIR", "America-AIR" ],
"country" : "USA",
"type" : "airline"} )
RETURNING META().id as docid, callsign[ARRAY_LENGTH(callsign)-1];[
{
"$1": "America-AIR",
"docid": "6af57793-65d2-4cc3-beea-5d713c7f3c29"
}
]Instead of providing actual values, you can specify the data to be inserted using the SELECT statement which selects the data from an existing keyspace.
Query the airport keyspace for documents with airportname "Heathrow", and then insert the projection (1 document) into the airport keyspace using a unique key generated using UUID().
INSERT INTO airport (KEY UUID(), VALUE _airport)
SELECT _airport FROM airport _airport
WHERE airportname = "Heathrow"
RETURNING *;[
{
"airport": {
"airportname": "Heathrow",
"city": "London",
"country": "United Kingdom",
"faa": "LHR",
"geo": {
"alt": 83,
"lat": 51.4775,
"lon": -0.461389
},
"icao": "EGLL",
"id": 507,
"type": "airport",
"tz": "Europe/London"
}
}
]Query the airport keyspace for documents with airportname "Heathrow", and then insert the projection into the airport keyspace using a unique key and an expiration of 2 hours.
INSERT INTO airport
(KEY UUID(), VALUE doc, OPTIONS {"expiration": 2*60*60})
SELECT a AS doc FROM airport a
WHERE airportname = "Heathrow";If you want to copy the expiration of an existing document to the inserted document, you can use a META().expiration expression in the SELECT statement, as shown here.
INSERT INTO airport
(KEY UUID(), VALUE doc, OPTIONS {"expiration": ttl})
SELECT META(a).expiration AS ttl, a AS doc FROM airport a
WHERE airportname = "Heathrow";Generate a document key as a combination of the projection and some function, such as <countryname>::<system-clock>.
The SELECT statement retrieves the country name "k1" and concatenates it with a delimiter "::" and the system clock function using the string concat operator "||".
INSERT INTO airport (KEY k1||"::"||clock_str(), value t)
SELECT DISTINCT t.country AS k1,t
FROM airport t
LIMIT 5
RETURNING META().id as docid, *;The result shows the META().id generated as a result of this concatenation (highlighted below).
[
{
"airport": {
"airportname": "Calais Dunkerque",
"city": "Calais",
"country": "France",
"faa": "CQF",
"geo": {
"alt": 12,
"lat": 50.962097,
"lon": 1.954764
},
"icao": "LFAC",
"id": 1254,
"type": "airport",
"tz": "Europe/Paris"
},
"docid": "France::2021-02-09T13:53:28.445Z"
}
]Use the INSERT statement to create a copy of keyspace_1 under the new name keyspace_2.
INSERT INTO keyspace_2(key _k, value _v)
SELECT META().id _k, _v
FROM keyspace_1 _v;Sub-queries can be used with INSERT in the insert-select form of the statement.
The SELECT part can be any sophisticated query in itself.
Insert a new type in documents from all hotels in the cities that have landmarks.
INSERT INTO hotel (KEY UUID()) (3)
SELECT x.name, x.city, "landmark_hotels" AS type (2)
FROM hotel x
WHERE x.city WITHIN
( SELECT DISTINCT t.city (1)
FROM landmark t)
LIMIT 4
RETURNING *;| 1 | The inner most SELECT finds all cities that have landmarks. |
| 2 | The outer SELECT finds the hotels that are in the cities selected by the inner query in Step 1.
It also adds a new type attribute with the value "landmark_hotels" to the projected result.
For brevity, we SELECT only 4 documents. |
| 3 | Finally, the INSERT statement inserts the result of Step 2 with UUID() generated keys. |
[
{
"hotel": {
"city": "Aberdeenshire",
"name": "Castle Hotel",
"type": "landmark_hotels"
}
},
{
"hotel": {
"city": "Aberdeenshire",
"name": "Two Bears Cottage",
"type": "landmark_hotels"
}
},
{
"hotel": {
"city": "Agoura Hills",
"name": "Malibu Creek Campground",
"type": "landmark_hotels"
}
},
{
"hotel": {
"city": "Altrincham",
"name": "Cresta Court Hotel",
"type": "landmark_hotels"
}
}
]Set the parameter $faa_code using the cbq prompt, or the Run-Time Preferences in the Query Workbench.
\SET -$faa_code "blr" ;INSERT INTO airport (KEY, VALUE)
VALUES ("airport_" || UUID(), (1)(2)
{ "type" : "airport",
"tz" : "India Standard Time",
"country" : "India",
"faa" : UPPER($faa_code)} ) (3)
RETURNING *;The query uses multiple functions during the INSERT:
| 1 | UUID() function to generate unique key for the document being inserted. |
| 2 | The string concatenation operator || to join "airport_" and the UUID. |
| 3 | UPPER string function to insert only uppercase values of the FAA code. |
{
"requestID": "4fea5296-c9f4-4fd3-be78-95e5a04531eb",
"signature": {
"*": "*"
},
"results": [
{
"airport": {
"country": "India",
"faa": "BLR",
"type": "airport",
"tz": "India Standard Time"
}
}
],
"status": "success",
"metrics": {
"elapsedTime": "7.7853ms",
"executionTime": "7.6472ms",
"resultCount": 1,
"resultSize": 167,
"serviceLoad": 4,
"mutationCount": 1
}
}Prepare an INSERT statement and execute it by passing parameters.
The INSERT statement has some of the attribute values preset while it takes the document key and airport faa_code as parameters.
First, prepare the INSERT statement.
PREPARE ins_india FROM
INSERT INTO airport (KEY, VALUE)
VALUES ( $key,
{ "type" : "airport",
"tz" : "India Standard Time",
"country" : "India",
"faa" : $faa_code} )
RETURNING *;Now execute the prepared statement using the cbq shell or the Query Workbench, passing the parameters key and faa_code.
EXECUTE ins_india
USING {"key": "airport_10001", "faa_code": "DEL"};[
{
"airport": {
"country": "India",
"faa": "DEL",
"type": "airport",
"tz": "India Standard Time"
}
}
]Alternatively, execute the prepared statement using the REST API, passing $key and $faa_code as REST parameters.
curl -v http://localhost:8093/query/service -u Administrator:password \
-d 'prepared="ins_india"&$key="airport_10002"&$faa_code="BLR"'{
"requestID":"55ff7e8a-7410-470f-ab83-c464f9d0092d",
"signature":{
"*":"*"
},
"results":[
{
"airport":{
"country":"India",
"faa":"BLR",
"type":"airport",
"tz":"India Standard Time"
}
}
],
"status":"success",
"metrics":{
"elapsedTime":"22.6797ms",
"executionTime":"17.0216ms",
"resultCount":1,
"resultSize":87,
"serviceLoad":4,
"mutationCount":1
}
}Explain Plan
To understand how the INSERT statement is executed by SQL++, let us take a look at two examples. For detailed explanation about the EXPLAIN plan, see the EXPLAIN statement.
To try the examples in this section, set the query context to the inventory scope in the travel sample dataset.
For more information, see Query Context.
EXPLAIN INSERT INTO airline (KEY,VALUE)
VALUES ( "1025",
{ "callsign": "SKY-AIR",
"country": "United States",
"id": "1025",
"type": "airline"
} ),
VALUES ( "1026",
{ "callsign": "F1-AIR",
"country": "United States",
"id": "1014"
} )
RETURNING *;{
"requestID": "5d1797cb-a7df-409d-b924-130ba0cc597a",
"signature": "json",
"results": [
{
"plan": {
"#operator": "Sequence",
"~children": [
{
"#operator": "ValueScan",
"cardinality": 2,
"cost": 0.032,
"values": "[[\"1025\", {\"callsign\": \"SKY-AIR\", \"country\": \"United States\", \"id\": \"1025\", \"type\": \"airline\"}], [\"1026\", {\"callsign\": \"F1-AIR\", \"country\": \"United States\", \"id\": \"1014\"}]]"
},
{
"#operator": "Parallel",
"maxParallelism": 1,
"~child": {
"#operator": "Sequence",
"~children": [
{
"#operator": "SendInsert",
"alias": "airline",
"bucket": "travel-sample",
"keyspace": "airline",
"namespace": "default",
"scope": "inventory"
},
{
"#operator": "InitialProject",
"result_terms": [
{
"expr": "self",
"star": true
}
]
}
]
}
}
]
},
"text": "INSERT INTO airline (KEY,VALUE) VALUES ( \"1025\", { \"callsign\": \"SKY-AIR\", \"country\": \"United States\", \"id\": \"1025\", \"type\": \"airline\" } ), VALUES ( \"1026\", { \"callsign\": \"F1-AIR\", \"country\": \"United States\", \"id\": \"1014\" } ) RETURNING *;"
}
],
"status": "success",
"metrics": {
"elapsedTime": "6.5577ms",
"executionTime": "6.2773ms",
"resultCount": 1,
"resultSize": 1898,
"serviceLoad": 4
}
}The query engine first scans the input values shown by the operator ValueScan to obtain the input values, and then it inserts the documents into the specified keyspace (shown by the operator SendInsert).
EXPLAIN INSERT INTO airport (key UUID(), value airport)
SELECT airport FROM airport
WHERE airportname = "Heathrow";[
{
"plan": {
"#operator": "Sequence",
"~children": [
{
"#operator": "Sequence",
"~children": [
{
"#operator": "IndexScan3", (1)
"bucket": "travel-sample",
"index": "def_inventory_airport_airportname",
"index_id": "14b05d2b21bd6eee",
// ...
},
{
"#operator": "Fetch", (2)
"bucket": "travel-sample",
"keyspace": "airport",
"namespace": "default",
"scope": "inventory"
},
{
"#operator": "Parallel",
"~child": {
"#operator": "Sequence",
"~children": [
{
"#operator": "Filter", (3)
"condition": "((`airport`.`airportname`) = \"Heathrow\")"
},
// ...
]
}
}
]
},
{
"#operator": "Parallel",
"~child": {
"#operator": "Sequence",
"~children": [
{
"#operator": "SendInsert", (4)
"alias": "airport",
"bucket": "travel-sample",
"key": "uuid()",
"keyspace": "airport",
"namespace": "default",
"scope": "inventory",
"value": "`airport`"
},
// ...
]
}
}
]
},
"text": "INSERT INTO airport (key UUID(), value airport)\n SELECT airport FROM airport\n WHERE airportname = \"Heathrow\";"
}
]The Query Engine first executes the SELECT statement and then uses the projection to insert into the airport keyspace, performing the operations in the order listed:
| 1 | An IndexScan to search for documents using the def_inventory_airport_airportname index. |
| 2 | A Fetch for the document in the airport keyspace. |
| 3 | A Filter for documents with airportname="Heathrow". |
| 4 | An Insert of the value along with the auto-generated key into the airport keyspace. |